Dopaminergic system
Neurotransmitter dopamine drives reward happiness and pleasure.
Dopamine is synthesized in multiple brain regions. One such region helps initiate movement;
Another regulates the release of a pituitary hormone.
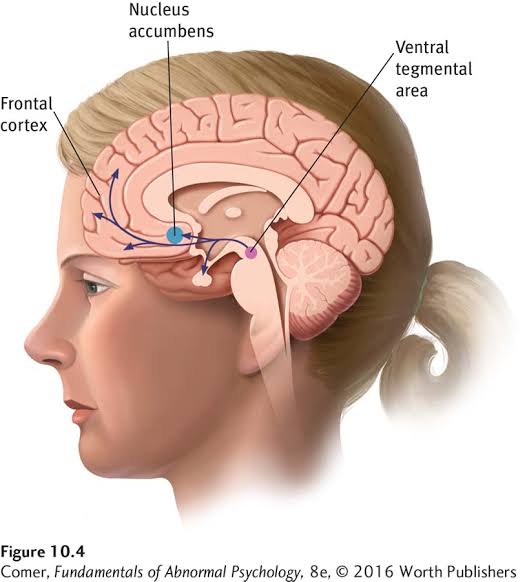
And another region is ventral tegmental area (henceforth the “tegmentum”).
These target nucleus accumbens (henceforth the “accumbens”).
The tegmentum sends projections to the accumbens and (other) limbic areas such as the amygdala and hippocampus. This is collectively called the “mesolimbic dopamine pathway.
The tegmentum also projects to the PFC (but, significantly, not other cortical areas). This is called the “mesocortical dopamine pathway.”
Winning a lottery and winning a bid both activated dopaminergic signaling in subjects; losing a lottery had no effect, while losing a bidding war inhibited dopamine release.
dopamine system gives insights into jealousy, resentment, and invidiousness
dopamine system is bidirectional.88 It responds with scale-free increases for unexpected good news and decreases for bad.
In one study subjects were shown an item to purchase, with the degree of accumbens activation predicting how much a person would pay.89 Then they were told the price; if it was less than what they were willing to spend, there was activation of the emotional vmPFC; more expensive, and there’d be activation of that disgust-related insular cortex
once reward contingencies are learned, dopamine is less about reward than about its anticipation
The domapmine system is more about anticipated reward, dopamine levels start rising, driven by the uncertainty of “maybe yes, maybe no.”
The circumstance with less information (i.e., that was more about ambiguity than risk) activated the amygdala and silenced dopaminergic signaling; what is perceived to be well-calibrated risk is addictive, while ambiguity is just agitating.
If you destroy its accumbens, a rat makes impulsive choices, instead of holding out for a delayed larger reward
Dopamine is not just about reward anticipation; it fuels the goal-directed behavior needed to gain that reward
It’s about the happiness of pursuit of reward that has a decent chance of occurring
contemplating the immediate reward activates limbic targets of dopamine (i.e., the mesolimbic pathway), whereas contemplating the delayed reward activates frontocortical targets (i.e., the mesocortical pathway)
This reveals how dopamine fuels delayed gratification. If waiting X amount of time for a reward has value Z; waiting 2X should logically have value ½Z; instead we “temporally discount”—the value is smaller, e.g., ¼Z. We don’t like waiting
Discounting curves—a value of ¼Z instead of ½Z—are coded in the accumbens, while dlPFC and vmPFC neurons code for time delay