amygdala
The Amygdala
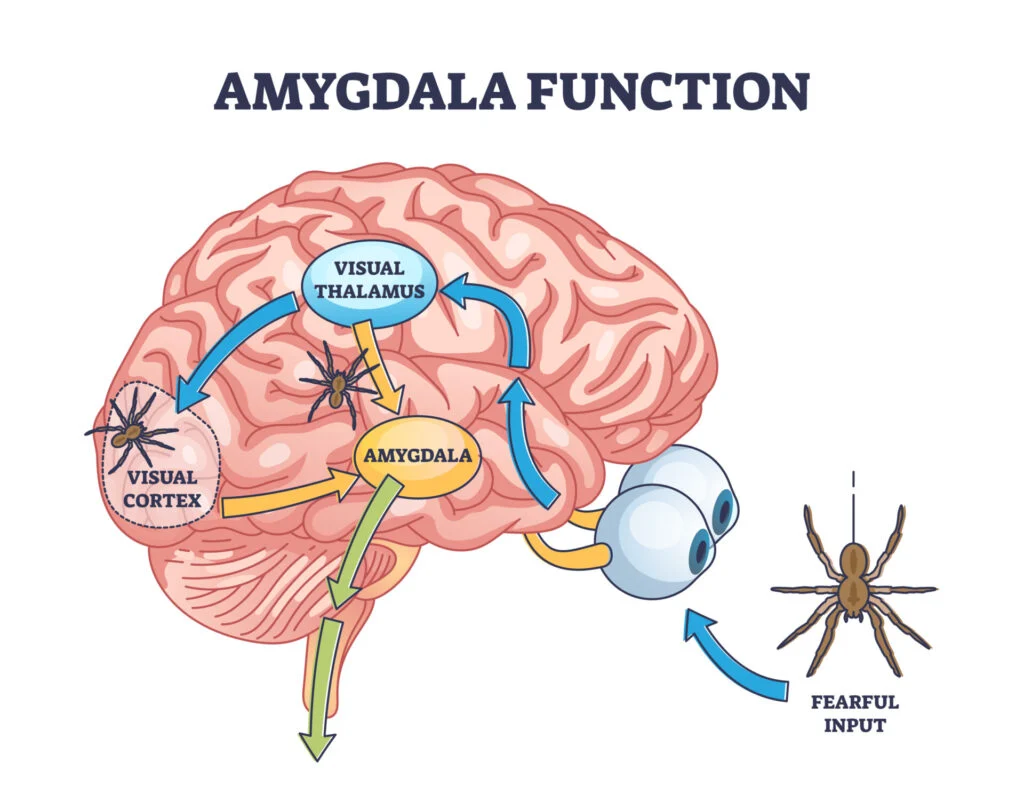
Relates to fear and anxiety.
The more activation of amygdala, the more fear and anxiety is felt.
The amygdala is sensitive to unsettling social circumstances, social uncertainty.
Being unsure of your place in social network is unsettling.
In PTSD patients, the amygdala is overreactive.
The basolateral amygdala surrounds the amygdala.
It is relatively newer part of the brain.
This part learns fear and sends this input to amygdala.
It never forgets this learning.
When we stop fearing something which we learnt to fear in the past, it's because we learned not to fear it actively and not actually forgot it.
The default state is to trust and amygdala learns vigilance and distrust.
Inputs to the amygdala
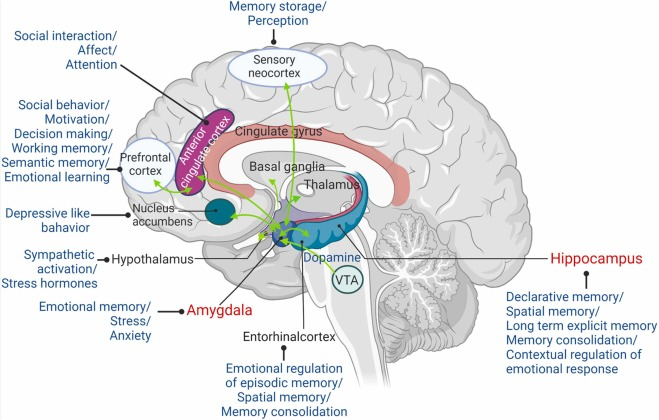
Sensory inputs
The BLA is directly connected to unpredictable pain neurons.
Information on pain
The PAG provides information on unpredictable pain to amygdala.
Disgust
Projections from insular cortex, provides information on rancid food and makes you spit out.
Outputs from amygdala
Mostly it is about setting alarms throughout the body.
Hippocampus
Amygdala learns fear and hippocampus learns context.
Hippocampus learns the context of fear.
Motor outputs
Normally amygdala talks to Frontal Cortex on mobilizing the body.
But, in extreme circumstances it can directly ask motor nerves to perform something.
Arousal
The BNST projects to hypothalmus to initiate stress response.
Both sex and aggression activates the Sympathetic Nervous System.